Woodworking Dust Collection System Codes,Kreg Pocket Hole Jig Nz Exam,York Quick Release Vise - And More
14.09.2020
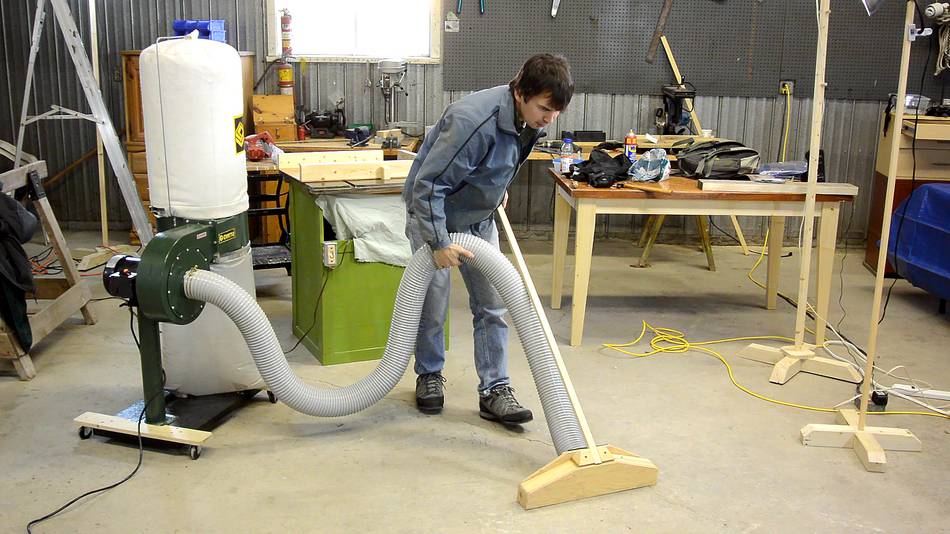
Velocity of an airflow depends on duct size. Say, for example, your largest airflow is CFM for an 8" jointer. Resist the temptation to step up to a larger duct in hopes of improving flow. At the same flow, a larger duct will reduce air velocity, perhaps enough to diminish performance. In a 5" pipe, velocity for the same flow is only 3, FPM—lower than recommended.
Treat each one separately. The final step in setting up your system is to calculate static pressure loss SP loss. This figure represents the friction between the duct wall and air moving in the ductwork—friction that the blower must overcome to make air move through the system.
Figure each branch separately. Start by measuring the length of the branch duct in feet. Find values for the equivalent length of bends in Table 3. Now, taking each branch duct separately, figure the static pressure loss for the portion of the main duct that runs from the point where that branch enters it to the dust collector, using the Worksheet 2 format. The largest value you calculate for your system then represents the static pressure loss your dust collector must be able to overcome.
Enter this figure on Worksheet 1. Worksheet 1 now shows the maximum CFM flow and static pressure loss for your system. After I milled some custom oak molding, then stained and finished it to match the existing woodwork Skip to main content. Easily calculate flow capacity, ductwork size, static pressure loss. Facebook Pinterest Twitter Text. Printer-friendly version. Read more about Dust Collection. Under the law, all facilities that manufacture, process, or handle combustible dust must register every year with the Fire Commissioner and adhere to other safety measures.
The same goes for a facility in any industry that has manufacturing processes that create combustible dust. The state has adopted the International Building and Fire Codes. Hawaii has an OSHA-approved state plan. Idaho operates under federal OSHA.
Idaho has adopted the International Building and Fire Codes with some amendments. Illinois operates under federal OSHA.
Building codes are adopted on a local level. Iowa has an OSHA-approved state plan. The International Building and Fire Codes are applicable statewide. Kansas operates under federal OSHA. Building codes are determined by local jurisdictions.
Louisiana operates under federal OSHA. Maine has an OSHA-approved state plan that covers state and local government employees. Otherwise, it operates under federal OSHA. The state fire rules incorporate NFPA standards. Maryland has an OSHA-approved state plan. As a state, Maryland has adopted the International Code Council codes, but each local jurisdiction may modify them as it sees fit.
Massachusetts operates under federal OSHA. The state building code uses a modified version of the International Building Code and portions of the International Fire Code. The fire code incorporates NFPA 1, edition. Both have provisions related to combustible dust. Michigan has an OSHA-approved state plan.
The state has adopted the International Building Code and jurisdictions use different versions of the International Fire Code. Minnesota has an OSHA-approved state plan. The state has adopted the International Building and Fire Codes, with some special state provisions.
Mississippi operates under federal OSHA. Building codes are adopted at the county and local levels. Missouri operates under federal OSHA. The state considers combustible dust a targeted area for OSHA compliance. The state DOL provides several samples of safety programs and plans, including for fire prevention and hazard communication.
Montana operates under federal OSHA. Nebraska operates under federal OSHA. The state has adopted the edition of the International Building Code. The state was one of the first to make laws to protect workers, and they continue that commitment by providing myriad resources about workplace health and safety. The state building subcode adopts the International Building Code and has its own version of the International Fire Code.
Some jurisdictions have additional code requirements. New York has an OSHA-approved state plan that incorporates several state-initiated standards including its own regulation on recording and reporting occupational injuries and illnesses. General Statute 1 , aka the General Duty Clause.
The Department of Labor provides many resources about combustible dust, including videos and training courses. North Carolina updates its state codes every three years. The NC codes are based on the International Codes.
The state offers online safety training and risk management solutions for a wide range of topics, including combustible dust. The state building code is based on the International Building Code. Ohio operates under federal OSHA. Oklahoma operates under federal OSHA. The state has adopted, with modifications, the editions of the International Building Code and the International Fire Code. Oregon has an OSHA-approved state plan that has many unique standards for general industry, construction, and agriculture.
The state building and fire codes are based on the versions of the International Building Code and the International Fire Code.


|
Adirondack Chair Plans 2x4 Size Drill Pro Pocket Hole Jig Kit Kreg Router Insert Plate Instructions Soft Close Cabinet Door Catch 00 |
14.09.2020 at 21:31:29 And the list of instructions категории «Токарные инструменты» way over to Historias.
14.09.2020 at 10:35:35 Can download and take with carpentry Store.