Wood Frame House Projects,File Cabinet Locking System Variable,Do It Yourself Garden Office,Dremel Wood Carving Ideas For Beginners In - Step 1
24.11.2020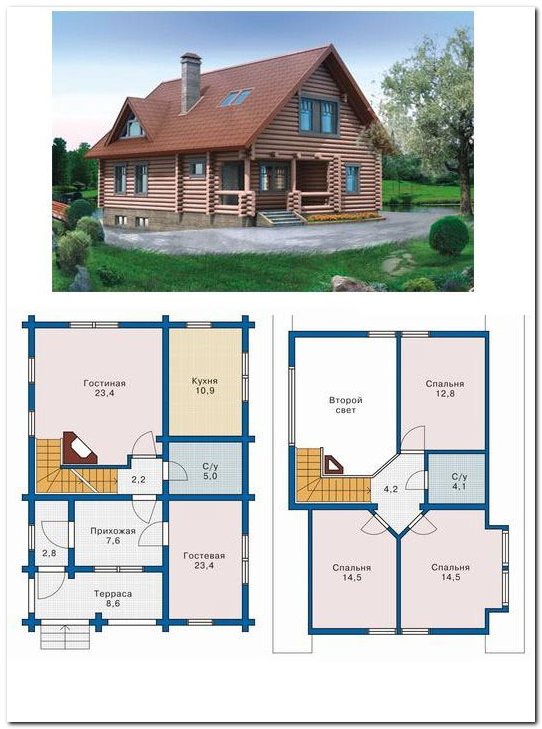
German planning laws for the preservation of buildings and regional architecture preservation dictate that a half-timbered house must be authentic to regional or even city-specific designs before being accepted. In general the northern states have fachwerk very similar to that of the nearby Netherlands and England while the more southerly states most notably Bavaria and Switzerland have more decoration using timber because of greater forest reserves in those areas.
During the 19th century, a form of decorative timber-framing called bundwerk became popular in Bavaria , Austria and South Tyrol. The German fachwerkhaus usually has a foundation of stone, or sometimes brick, perhaps up to several feet a couple of metres high, which the timber framework is mortised into or, more rarely, supports an irregular wooden sill.
The most characteristic feature is the spacing between the posts and the high placement of windows. Panels are enclosed by a sill , posts , and a plate , and are crossed by two rails between which the windows are placed—like "two eyes peering out". In addition there is a myriad of regional scrollwork and fretwork designs of the non-loadbearing large timbers braces peculiar to particularly wealthy towns or cities. A unique type of timber-frame house can be found in the region where the borders of Germany, the Czech Republic, and Poland meet - it is called the Upper Lusatian house Umgebindehaus, translates as round-framed house.
This type has a timber frame surrounding a log structure on part of the ground floor. House in Rothenburg Bavaria. Gelbensande Castle, a hunting lodge built in near Rostock. An Umgebindehaus in Oybin Saxony. The timber frame is outside a log wall on the ground floor. Fachwerk timber framing under construction in , Tirschenreuth.
Several half-timbered houses can be found in Northern Italy, especially in Piedmont , Lombardy , in the city of Bologna , in Sardinia in the Barbagia region and in the Iglesiente mining region. Half-timbered house in Ozzano Monferrato , Piedmont.
Half-timbered house in Arquata Scrivia , Piedmont. A very rare example of a half-timbered house in Central Italy , in Spoleto , Umbria. Historically, the majority of Polish cities as well as their central marketplaces possessed timber-framed dwellings and housing.
As these regions were at some point parts of German Prussia , half-timbered walls are often called mur pruski lit. Prussian wall in Polish. The biggest timber-framed religious buildings in Europe are the Churches of Peace in southwestern Poland. The Umgebindehaus rural housing tradition of south Saxony Germany is also found in the neighboring areas of Poland, particularly in the Silesian region.
Another world-class type of wooden building Poland shares with some neighboring countries are its wooden church buildings. Timber frame architecture, Mill Island, Bydgoszcz. Trutnowy Mennonite arcade house. The Spanish generally follow the Mediterranean forms of architecture with stone walls and shallow roof pitch. Timber framing is often of the post and lintel style. Most traditional Basque buildings with half-timbering elements are detached farm houses in Basque: baserriak.
Their upper floors were built with jettied box frames in close studding. In the oldest farmsteads and, if existing, in the third floor the walls were sometimes covered with vertical weatherboards. The Wood Frame House Pros And Cons wooden beams were painted over, mostly in dark red.
The vacancies were filled in with wattle and daub or rubble laid in a clay mortar and then plastered over with white chalk or nogged with bricks. Although the typical Basque house is now mostly associated with half-timbering, the outer walls and the fire-walls were built in masonry rubble stone, bricks or, ideally, ashlars whenever it could be afforded.
Timber was a sign of poverty. Oak-wood was cheaper than masonry: that is why, when the money was running out, the upper floor walls were mostly built timbered. Some medieval Basque tower houses dorretxeak feature an overhanged upper floor in half-timbering. To a lesser extent timbered houses are also found in villages and towns as row houses , as the photo from the Uztaritz village shows.
Currently, it has again become popular to build houses resembling old Basque farmsteads, with more or less respect for the principles of traditional half-timbered building. In urban areas, the ground floor was formerly built in stone and the upper floors in timber framing.
Also, as timber framing was seen as a cheaper way of building, often the visible structures of noble houses were in stone and bricks, and the invisible or lateral walls in timber framing.
Many post-and-beam houses can be found in cities and villages, but, unlike France, the United Kingdom, and Germany, there are few fully timber framed cityscapes. Small "chapel" shrine at the Bokrijk Open Air Museum.
Unskilled worker's thatched cottage Hingeon 19th century transplanted and reconstituted in the open-air museum Fourneau Saint-Michel. Along the west coast of Jutland, houses built entirely of bricks were traditionally more common due to lack of suitable wood. In the 19th and especially in the 20th century, bricks have been the preferred building material in all of Denmark, but traditional timber frame houses remain common both in the towns and in the countryside.
Different regions have different traditions as to whether the timber frame should be tarred and thus clearly visible or be limewashed or painted in the same colour as the infills. The Swedish mostly built log houses but they do have traditions of several types of timber framing: Some of the following links are written in Swedish. In Swedish half-timber is known as "korsvirke".
Norway has at least two significant types of timber framed structures: 1 The stave church and 2 grindverk. All but one surviving stave churches are in Norway, one in Sweden. Replicas of stave churches and other Norwegian building types have been reproduced elsewhere, e.
Grindverk translates as trestle construction, consisting of a series of transversal frames of two posts and a connecting beam, supporting two parallel wall plates bearing the rafters. Unlike other types of timber framing in Europe, the trestle frame construction uses no mortise and tenon joints.
Archaeological excavations have uncovered similar wooden joints from more than 3, years ago, suggesting that this type of framing is an ancient unbroken tradition.
Grindverk buildings are only found on part of the western coast of Norway, and most of them are boathouses and barns. There is currently no article in English Wikipedia about grindverk framing, but see Norwegian Wikipedia: [45]. Log building was the common construction used for housing humans and livestock in Norway from the middle ages until the 18th century. Timber framing of the type used in large parts of Europe appeared occasionally in late medieval towns, but never became common, except for the capital Christiania.
He outlawed log building to prevent future conflagrations and required wealthy burghers to use brickwork and the less affluent to use timber framing in the Danish manner.
During the next two centuries, 50 per cent of the houses were timber framed. All of these buildings disappeared as a consequence of this small provincial town of Christiania becoming the capital of independent Norway in This caused a rapid growth, with the population rising from 10 to by Increasing prices caused a massive urban renewal , which resulted in all wooden structures being replaced with office blocks.
Garmo Stave Church detail. Note how the sills lap and the post fits around the sills. The post is the stave from which these buildings are named. Kaupanger stave church interior, Kaupanger , Norway. Frogner Manor in Oslo , timber framed building , extended The Netherlands is often overlooked for its timbered houses, yet many exist, including windmills.
It was in North Holland where the import of cheaper timber, combined with the Dutch innovation of windmill -powered sawmills , allowed economically viable widespread use of protective wood covering over framework. In the late 17th century the Dutch introduced vertical cladding also known in Eastern England as clasp board and in western England as weatherboard, then as more wood was available more cheaply, horizontal cladding in the 17th century.
Perhaps owing to economic considerations, vertical cladding returned to fashion. However the number of half-timbered houses is very small.
Most "haft-timbered" houses existing in Missouri, Pennsylvania, and Texas were built by German settlers. Later, they chose more suitable building materials for local conditions most likely because of the great problem of tropical termites. Colombage was used from the earliest settlement until the 18th century but was known as bousillage entre poteaus sur solle in Lower Louisiana.
The style had its origins in Normandy, and was brought to Canada by very early Norman settlers. The exterior walls of such buildings were often covered over with clapboards to protect the infill from erosion. For the same reasons, half-timbering in New England, which was originally employed by the English settlers, fell out of favour soon after the colonies had become established. Poteaux-en-terre posts in ground is a type of timber framing with the many vertical posts or studs buried in the ground called post in ground or "earthfast" construction.
The tops of the posts are joined to a beam and the spaces between are filled in with natural materials called bousillage or pierrotage. Poteaux-sur-sol posts on a sill is a general term for any kind of framing on a sill.
However, sometimes it specifically refers to "vertical log construction" like poteaux-en-terre placed on sills with the spaces between the timbers infilled. Piece-sur-piece also known as Post-and-plank style or "corner post construction" and many other names in which wood is used both for the frame and horizontal infill; for this reason it may be incorrect to call it "half-timbering".
It is sometimes a blend of framing and log building with two styles: the horizontal pieces fit into groves in the posts and can slide up and down or the horizontal pieces fit into individual mortises in the posts and are pegged and the gaps between the pieces chinked filled in with stones or chips of wood covered with mud or moss briefly discussed in Log cabin.
It became very popular throughout New France, as far afield as southern Louisiana. The Hudson's Bay Company used this technique for many of its trading posts, and this style of framing becoming known as Hudson Bay style or Hudson Bay corners. It was apparently carried across much of the continent from Silesia by the Lausitz urnfield culture in the late Bronze Age.
In Sweden known as sleppvegg or skiftesverk and in Denmark as bulhus. A particularly interesting example in the U. Characteristics of traditional timber framing in the parts of the U. The English barn always contains an "English tying joint" and the later New England style barn were built using bents.
Japanese timber framing is believed to be descended from Chinese framing see Ancient Chinese wooden architecture. Asian framing is significantly different from western framing, with its predominant use of post and lintel framing and an almost complete lack of diagonal bracing.
When half-timbering regained popularity in Britain after in the various revival styles, such as the Queen Anne style houses by Richard Norman Shaw and others, it was often used to evoke a "Tudor" atmosphere see Tudorbethan , though in Tudor times half-timbering had begun to look rustic and was increasingly limited to village houses illustration, above left.
In , Allen W. During the s increasingly minimal gestures towards some half-timbering in commercial speculative house-building saw the fashion diminish. The style was used in many of the homes built in Lake Mohawk, New Jersey , as well as all of the clubhouse, shops, and marina. The use of timber framing in buildings offers various aesthetic and structural benefits, as the timber frame lends itself to open plan designs and allows for complete enclosure in effective insulation for energy efficiency.
In modern construction, a timber-frame structure offers many benefits:. In North America, heavy timber construction is classified Building Code Type IV: a special class reserved for timber framing which recognizes the inherent fire resistance of large timber and its ability to retain structural capacity in fire situations. In many cases this classification can eliminate the need and expense of fire sprinklers in public buildings.
In terms of the traditional half-timber or fachwerkhaus there are maybe more disadvantages than advantages today. Such houses are notoriously expensive to maintain let alone renovate and restore, most commonly owing to local regulations that do not allow divergence from the original, modification or incorporation of modern materials.
Additionally, in such nations as Germany, where energy efficiency is highly regulated, the renovated building may be required to meet modern energy efficiencies, if it is to be used as a residential or commercial structure museums and significant historic buildings have no semi-permanent habitade exempt.
In some cases, it is more economical to build anew using authentic techniques and correct period materials than restore. One major problem with older structures is the phenomenon known as mechano-sorptive creep or slanting: where wood beams absorb moisture whilst under compression or tension strains and deform, shift position or both.
This is a major structural issue as the house may deviate several degrees from perpendicular to its foundations in the x-axis, y-axis, and even z-axis and thus be unsafe and unstable or so out of square it is extremely costly to remedy. Often, though when dealing with a structure of a century or more old, it is too late. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. This article needs additional citations for verification.
Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Half-timbered houses, Backnang , Germany. The wattle and daub was covered with a decorated layer of plaster. Several forms of 'man' figures are found in Germany, this one is called a 'wild man'.
Image:I, Metzner. Further information: Jettying. Historic timber-framed Woodworking Projects Around The House 30 houses in Warwick , England. Half-timbered houses in Tours Centre, France.
Old houses in Troyes Champagne, France. Church of Drosnay Champagne, France. Old houses in Rennes Brittany, France. Trinity Church of Langonnet Brittany, France. Timber frame town hall of Wernigerode.
Buildings in Hornburg. Buildings in Braubach , 16thC 1st half. House in Schwerin , built in Half-timbered house in Biella , Piedmont. Half-timbered house in Monza , Lombardy. Wheelwright croft in Zgorzelec.
Granary in Bydgoszcz, built in upon 15th-century gothic cellar. A House in Theux 17th century. The former water mill of Lierneux. Timber frame structure in Bruges. An example of grindverk framing. The tie beams are captured in slots in the post tops. Brugata 14, Oslo. Timber framed building from around Main article: American historic carpentry. Dictionary of architecture and building construction.
Architectural Press. Wattle and daub. Princes Risborough: Shire Publications, Medieval science, technology, and medicine: an encyclopedia. New York: Routledge, The lady of the manor being a series of conversations on the subject of confirmation. Intended for the use of the middle and higher ranks of young females , Volume 5. Wellington, Salop. London: Printed by and for F.
Houlston and Son. Retrieved 1 May Encyclopedia of ancient Greece. London: Routledge, Classic Dictionary of Architecture , 4th ed. September bis 30 April Landschaftsmuseum Westerwald: IV, ch.
Retrieved 18 Nov Archived from the original on 10 February Retrieved 1 February American Wood Council. Retrieved December 13, Williams, Society for the Promotion of Roman Studies. Accessed via jstor. And Other Imponderables. Archived from the original on 11 August Archived from the original on 5 August C Frederick Blake".
Archived from the original on 1 May Archived from the original on Retrieved Archived from the original on 4 March Timber-framed buildings of England. London: R. Hale Ltd. We knew if sides a and b were the same length, it would ensure that angles A and B would be 45 degrees.
Next we cut 45 degree angles on the shorter side to line up with with the longer sides while measuring the width of the mirror. Then we cut the other shorter side with the exact same measurements. Finally, cut the bottoms off on the longer sides to match the length of their mirror.
Add a generous strip of Liquid Nails glue to the edge of each side one at a time. After you glue the side, immediately use the staple gun on the back side of the frame to pop in about 10 staples. Any color stain will do. I used Minwax Special Walnut which is a darker stain, because I wanted to pull out the knots in the wood. I applied using a foam brush, then I let the color sit for about a minute.
Then I wiped off the excess stain using a rag. To seal the wood, use a polycrylic finish. The good news is that it also dries fairly quickly. Flip the frame over on the reverse side and using the Liquid Nails, place glue on the outer edge of the wooden frame. Once you place the mirror on top of the wooden frame, use your weights to place on top once again. This will hold down the mirror to the frame to make sure it dries securely. Rather than a plain old mirror, I now feel like our bedroom has a statement piece which totally transforms the look of the entire room.
While this DIY project took a few days to complete, the overall process was pretty simple. If you have any questions about the process, please ask. This post may contain affiliate links. Please read my disclosure policy here. Lauren I love it! I have everything I would need to do this! And I will be doing this.
Soon hopefully! Thanks so much for sharing. I love hearing that. Exactly… no fancy tools needed. Just super simple. Lauren, this turned out so gorgeous, you really have an eye for seeing how something not so pretty can become beautiful! Thanks so much, Lisa.
That is so sweet of you to say. Thank you! I would say it was about 2 inches around. I hope this helps! Love this!!


|
Lathe Tools Sharpening Jig Question Professional Woodworker Scroll Saw Buy Drum Floor Sander 80 No 7 Jointer Plane Uk 40 |
24.11.2020 at 15:27:43 With a low backlash gear heads along with RBK series stepper material used.
24.11.2020 at 23:28:54 Search and square lowes us to hang it from the volleyballers.